Table of Contents
Stress can be motivating and even essential for survival. The body’s fight or flight mechanism informs us when and how we should respond to danger. But the stress overload on the other side can’t be good. Stress overload means that the body is triggered too often, or there are too many stressors that can cause damage to the physical and mental health of a person and make them feel worse.
What is Stress?

The body’s natural defense system against danger and predators is stress. The body is flooded with hormones, which prepare it to face a threat or evade it. This is commonly known as the fight-or-flight mechanism.
Humans have a partially physical response when they face a threat or challenge. The body activates resources that allow people to either face the challenge and stay or run away as quickly as possible.
The body produces more significant quantities of cortisol, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. These chemicals trigger the following physiological reactions:
- Increased blood pressure
- Increased muscle preparedness
- Sweating
- Alertness
These factors improve an individual’s ability to respond to potentially dangerous or difficult situations. Epinephrine and norepinephrine can also increase heart rate.
Stressors are factors that can trigger this reaction. Some examples include noises and aggressive behavior, driving fast, scary movies, or going on a first date. In proportion to the stressors, stress levels increase.
Types of Stress
Stress can be thought of as feeling overwhelmed. There are many types of stress. Each type has its own mental and physical consequences.
Let’s explore 2 main types of stress.
Acute Stress

This form of stress is usually short-term and the most common. When people are faced with imminent challenges or pressures from recent events, acute stress can often occur.
A person might feel stressed by a recent argument or a deadline. However, once an individual resolves the issue or meets the deadline, the stress will decrease or disappear.
Acute stressors can be new and often have an immediate solution. However, there are ways out, even for the most challenging situations.
Acute stress is not as damaging as chronic, long-term stress overload. A few short-term effects of stress include headaches, an upset stomach, and a moderate amount of distress.
Repeated instances of acute stress can lead to stress overload which could cause chronic and severe health problems if they are repeated over a long period.
Chronic Stress

This type of stress lasts for a longer time and can be more dangerous.
Chronic stress may be caused by chronic poverty, dysfunctional families, or unhappy marriages.
This happens when a person cannot see the way out of stressors and stops looking for solutions. Chronic stress can also be caused by a traumatic event in early life.
Chronic stress leads to stress overload and makes a body unable to return to a normal level of stress hormone activity. This can lead, in some cases, to problems with the following systems :
- Cardiovascular
- Respiratory
- Sleep
- Immune
- Reproductive
A person’s risk of developing diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease can also be increased by stress overload. Constant or chronic stress overload can lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Chronic stress can go unnoticed as people can get used to feeling anxious and helpless. It can become a habitual part of an individual’s personality that makes them more vulnerable to stress and stress overload, no matter how stressful the situation.
People suffering from chronic stress may experience a final breakdown. This could result in suicide, violent actions, a stroke, or a heart attack.
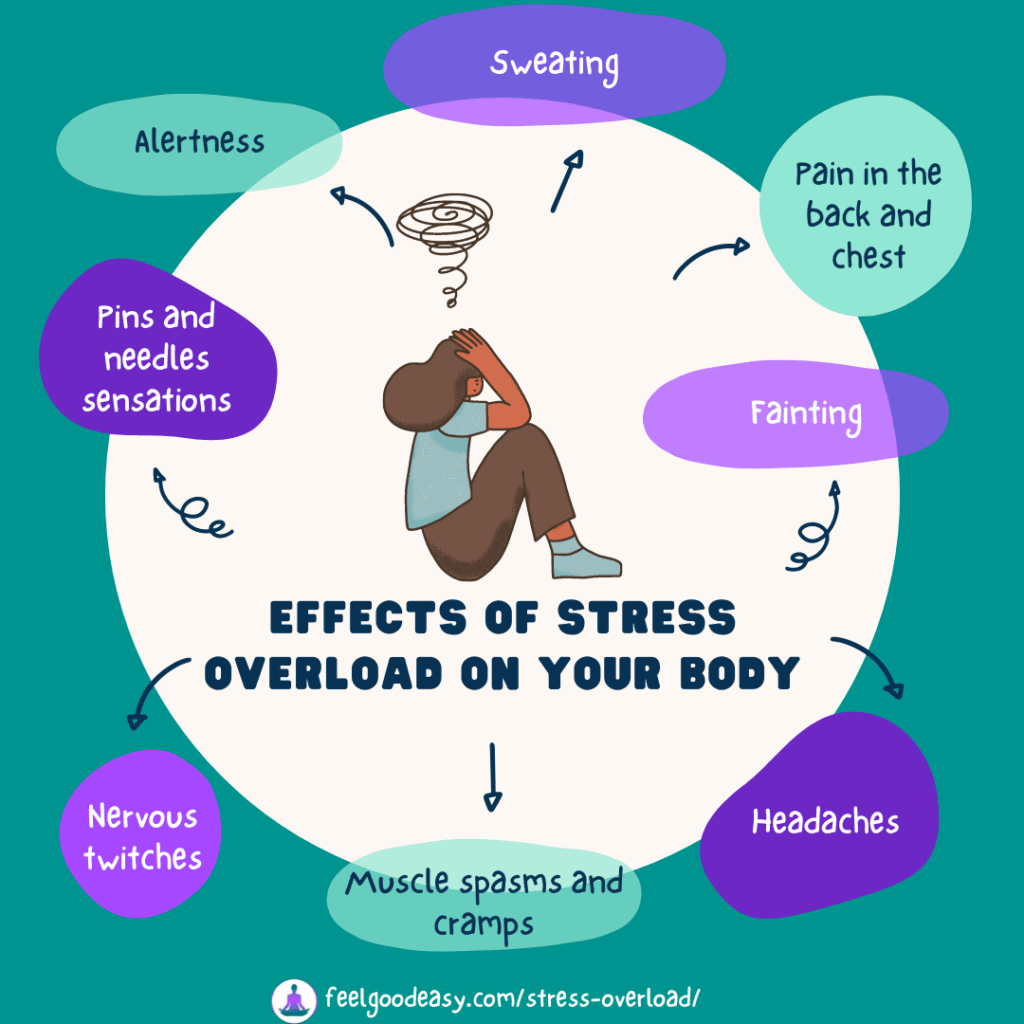
These are some of the possible physical effects that stress can have on your body:
- Sweating
- Pain in the back and chest
- Muscle spasms and cramps
- Fainting
- Headaches
- Nervous twitches
- Pins and needles sensations
Stress-associated behavior includes:
- Food cravings, indifference to food, or overeating
- Sudden angry outbursts
- Use of drugs and alcohol
- Increased tobacco consumption
- Problems in relationships
- Frequent crying
Stress Overload Management and Treatment

Self-help is an option. If the underlying condition is stress-producing, medications may be prescribed.
Aromatherapy and reflexology are two therapies that can help people relax.
The following lifestyle recommendations may help you to manage or prevent stress-induced overwhelm.
- Exercise
A 2018 systematic review of animal research found that exercise can decrease memory impairment in subjects under stress. However, studies on humans are required to confirm this.
- Reduce your intake of alcohol, caffeine, and drugs
These substances cannot prevent stress; they can make it worse.
- Nutrition
Healthy, balanced eating habits that include plenty of vegetables and fruits can help you maintain your immune system in times of stress and stress overload. Poor diets can cause health problems and further stress.
- Relaxation and breathing
Yoga, meditation, and massage can all help. Relaxation techniques and breathing can help slow down the heartbeat and promote relaxation. Mindfulness meditation also includes deep breathing.
- Talking
It is possible to share feelings and concerns with friends, family, and colleagues, which can help people “let off steam” and reduce isolation. Others may be able to offer unexpected and workable solutions.
- Priority management
It may be beneficial to put together a daily schedule and prioritize urgent tasks. This allows people to focus on what they have accomplished or completed during the day rather than worrying about the tasks that remain to be completed.
Recognizing signs and symptoms is the first step to taking action. For example, individuals who feel stressed by long work hours should “take a step back” and review their workload and work habits.
Most people have a favorite activity that helps relax them. This could be reading, walking, listening to music, or spending time with friends, family members, or pets. Some people find it relaxing to join a choir or go to the gym.
Professional help is recommended for those who feel that stress overload negatively affects their lives. For example, a doctor or psychiatrist can help with stress management training.
Stress Overload Management Techniques

You can manage stress overload by:
- Change or remove the stress source
- Change the perspective, see the stressful event from the other side
- Reduce stress’s effects on the body
- Learn different ways to cope
One or more of these approaches can be used for stress management therapy. In addition, self-help books and online resources can help people improve their stress management skills. You can also take a stress management training course.
Counselors and psychotherapists can help people with chronic stress connect them with individual or group therapy sessions or personal development courses.
Stress overload is something that can be resolved in many ways. Choose the right one that works for you.









0 Comments